Megatrend energy technologies
From the FMG Trend System: For your future-proof company
Energy technologies, a megatrend with economic explosive power
Global climate targets, geopolitical dependencies and rising energy demand pose major challenges for society and the economy. The energy technologies megatrend shows how technological progress is becoming the key driver of a sustainable energy supply. The shift towards electricity as the lead sector offers enormous efficiency gains. Electrification, digitalization and decentralization will reorganize the energy supply.
Energy is not just a cost factor, but increasingly a competitive factor. Companies that increase efficiency, secure supply and use new business models are creating advantages for themselves. At the same time, new technologies are creating entire markets – from storage solutions to the hydrogen economy. To the overview of all megatrends

What do energy technologies mean for companies?
Energy issues affect almost every industry today – directly or indirectly. Production processes, supply chains, mobility, buildings and IT infrastructures must be optimized for energy efficiency and security of supply. At the same time, new energy technologies are also opening up new business opportunities:
Suppliers can invest in new markets, e.g. charging infrastructure, storage systems or digital platforms. Users benefit from cost reductions, increased resilience and environmental advantages – often also as a competitive advantage in sales. Combiners develop innovative solutions from technology, data and services, for example in areas such as “Energy-as-a-Service” or virtual power plants.
The megatrend is giving rise to new value creation logics – from decentralized power grids to the cross-sector coupling of energy, mobility, IT and industry.
- Alongside human motives, energy technologies and other technologies are the most transformative trends. We use our tools to shape the world, mostly to our advantage.
- The energy technology megatrend is just one of many that could be relevant to the future of your business.
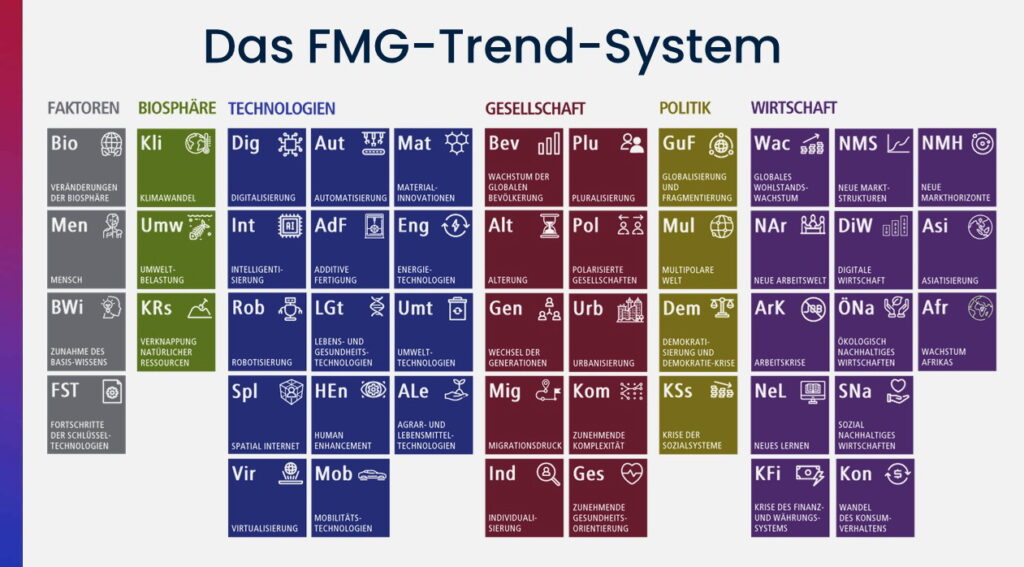
- In addition to megatrends from the biosphere, society, politics and the economy, FMG’s trend system also includes the drivers that trigger trends such as energy technologies, the future factors. To the overview of all megatrends
Four key developments in energy technologies
1. energy-saving technologies
Saving energy is the “invisible source” of sustainable supply. Advanced technologies make it possible to consume less energy – without sacrifice, but with efficiency. Important aspects are:
- Minimizing efficiency losses: If electricity is used to generate heat or motion instead of fossil fuels, fewer losses are caused by waste heat – electrified systems are therefore systemically more efficient.
Intelligent building control: Smart buildings automatically adapt heating, cooling and lighting to requirements.
Industrial efficiency: process optimization, heat recovery or intelligent machine control reduce consumption.
Energy-saving devices: More efficient chips, displays and control systems extend battery life and reduce electricity costs.
Mobility efficiency: Lighter vehicles, hybrid technology and better aerodynamics increase the range per kWh.
2. renewable energies
Renewable energies such as wind, sun, water and biomass are the foundation of the energy transition. They are available in unlimited supply, cause no emissions during operation and are becoming increasingly attractive economically thanks to innovations. The most important sub-trends are:
Photovoltaics: Advances in solar cells, solar films and quantum dot technologies reduce costs and expand fields of application.
Solar thermal energy: Use of solar energy to generate heat – can be efficiently stored for electricity or heating.
Wind power: Increasingly powerful onshore and offshore turbines are becoming the mainstay of the electricity supply.
Hydropower: From large-scale plants to small hydropower plants – an important backbone of renewable electricity generation, depending on the region.
Geothermal energy: low-emission heat and power generation regardless of the weather and time of day.
Bioenergy: Use of biomass, residual materials or biogas – particularly useful where there are no alternatives.
Maritime energy generation: wave, tidal and ocean current power plants complement offshore wind power.
Energy harvesting: tapping environmental energy from vibrations, heat differences or light for sensors and microelectronics.
Osmotic power: Utilization of salinity differences between freshwater and seawater to generate electricity.
3. more powerful energy storage systems
Volatile generation from solar or wind requires flexible and reliable storage solutions. The better electricity can be stored, the more secure and economical the energy system becomes.
Subtrends at a glance:
Lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries: standard for mobile and stationary storage – with increasing energy content.
Supercapacitors: Very fast-charging energy storage devices with high cycle stability for special applications.
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G): Electric vehicles serve as intermediate storage for the public grid.
Nuclear batteries: For special applications with extremely long runtimes – e.g. space travel or remote systems.
Paper batteries: Thin, flexible and resource-saving – suitable for IoT and medical technology.
Quantum Nucleonics: Theoretically possible use of nuclear isomers as extremely energy-dense storage – so far purely visionary.
4. smart grid
Smart grids control generation, consumption, storage and trading in real time. They are the control center of the decentralized, digital energy world.
Subtrends at a glance:
Smart metering: Intelligent metering systems enable dynamic tariffs, load management and transparency for users.
Virtual power plants: Combination of many small generators to form controllable energy clusters – e.g. for municipal utilities.
Energy platforms: Digital marketplaces network supply, demand, storage and grids in real time.
IT security for power grids: Cybersecurity is becoming a key prerequisite for the resilience of critical energy infrastructure.
Energy sharing & microgrids: Local grids enable the exchange of electricity between households, businesses and mobility.
Conclusion: Increase your own future security with energy technologies
Energy technologies are shaping key issues for the future: climate protection, competitiveness, security of supply.
- New technologies are opening up attractive business models – even outside the traditional energy sectors.
- Companies must not only react, but actively shape things: through innovation, partnerships and smart investments.
- With the Future Radar Program, you can see how energy technologies are changing your company and how you can use them as a strategic opportunity.